
Emerging technology can reduce CO2 emissions from air cooling systems, experts say
Scientists have been working to develop cost-effective technologies that reduce CO2 emissions.
Mar. 2, 2022Coverage begins in 2006 for the ScienceWriters meeting and 2009 for the AAAS meeting. To see programs for past ScienceWriters meetings, go to the ScienceWriters meeting site.

Scientists have been working to develop cost-effective technologies that reduce CO2 emissions.
Mar. 2, 2022
While many are familiar with climate change’s impact on marine ecosystems, new research is showing how phenomena like harmful algal blooms bring profound risks to human health, as well.
Mar. 2, 2022
Climate change and other human impacts on aquatic ecosystems also accelerate health risks for those living near rivers, lakes and marine coastal areas.
Mar. 2, 2022
In 2016, hundreds of volunteers in Kenya – school kids, park rangers, scientists, and tourists – took part in a two-day event called Great Grevy's Rally to help save the endangered Grevy’s Zebra.
Mar. 2, 2022
Health care practitioners, researchers, policymakers, and the public are banding together to study the ocean connection to public health and find ways to address and mitigate these emerging risks.
Mar. 2, 2022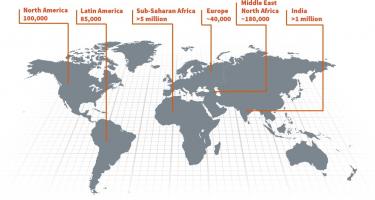
A newly developed gene therapy is showing very promising early clinical results for sickle cell disease.
Mar. 2, 2022Helen Mayberg, M.D., discussed the three markers her lab developed to monitor and define recovery in patients who have been successfully treated for treatment-resistant depression with deep brain stimulation (DBS).

Research from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York and Emory University in Atlanta is providing a new view of depression.

Face masks worn during the pandemic unveiled insights into the ways humans process and interact with faces, scientists say.

Mask-wearing raises critical questions: If we obscure the face, what would we focus on when seeing another person? How would we show emotions, or engage in conversation?